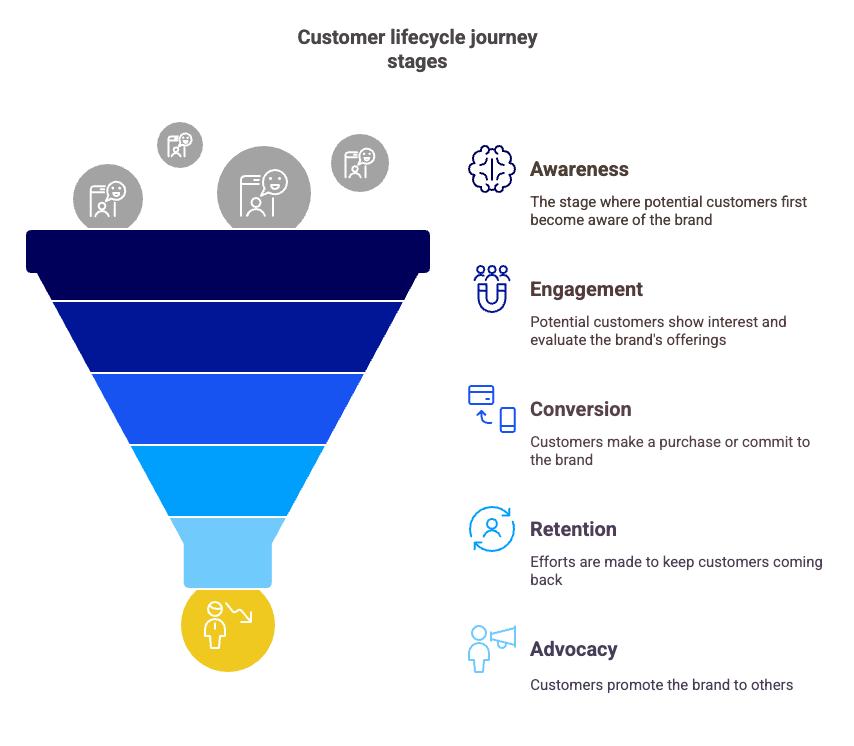
1. Awareness/reach
The awareness stage sits at the very top of the marketing funnel, where marketers build brand awareness through campaigns designed to reach new prospects and attract new website traffic — or foot traffic to a brick-and-mortar store. Potential customers in the awareness stage often know they need a product or service to address a specific pain point. However, they are either unaware of specific brands that offer solutions or unsure about what distinguishes one brand or product from another.
Common marketing activities at this stage include:
SEO-related tactics such as on-page website optimization and short-form, keyword-driven blog posts geared toward capturing organic search traffic and siphoning traffic away from competitors’ sites.
Advertising that creates a positive first impression of the brand on websites, social media platforms, podcasts, and radio or TV broadcasts popular with the target audience or billboards in locations frequented by them.
Partnering with influencers or cross-promoting content with a partner that has an overlapping target audience.
2. Engagement/acquisition/evaluation
A successful awareness campaign leads to brand engagement: Prospects discover the brand’s products and services, and express interest — by visiting the website, subscribing to an email list, following social media channels, or browsing the shelves at a store. At this stage, marketers help prospects make an informed decision with content and offers highlighting features, benefits, and cost-effectiveness.
Common content marketing strategies at this stage include:
Short, easy-to-understand product demos that address specific pain points and underscore key value propositions.
Long-form content such as best practices or buyer’s guides, ebooks, research-based white papers, and data-driven industry reports that highlight the need for the product and situate it as an industry leader.
Case studies that provide real-world proof of the product’s effectiveness.
In-store promotions like free samples.
3. Conversion
To move a prospect from evaluation to purchase, marketers make the purchasing experience as frictionless as possible and provide content that assures the customer they’re making a good decision.
Common conversion strategies include:
Optimized landing pages that offer clear, competitive pricing and make it easy to download a trial or freemium version of the product, access a discount offer, or make an initial purchase.
Providing customer testimonials that speak to the quality of the product and the brand’s customer service.
Email campaigns that reiterate special offers, reinforce the product’s value propositions, or remind shoppers on e-commerce sites about items that remain unpurchased in their carts.
4. Retention
Many marketers know it costs less to keep an existing customer than to capture a new one. Satisfied customers are often repeat customers, and customer retention is as important as lead generation. Successful customer retention campaigns can increase revenue and lifetime customer value by shaping a positive customer experience.
Strategies for the retention stage of the customer lifecycle include:
Making the product easy to use by providing easy-to-follow setup or onboarding materials and user guides, excellent customer service, FAQ pages, and customer-led troubleshooting forums.
Discount offers for additional purchases and new product announcements.
Email campaigns for upsells or cross-sells of complementary products.
5. Advocacy
Long-term customers are not only a reliable revenue stream: They can become brand ambassadors, references, and a source for case studies and testimonials. Successful retention strategies that lead to positive experiences can turn customers into advocates.
Advocacy and nurture tactics can include:
Product review requests and soliciting input on new product development.
Rewards, discounts, and customer loyalty programs for referrals or purchases.
Incentives for sharing testimonials on social media or participating in case studies.
Raising the industry visibility of loyal customers through webinars, seminars, and events.
6. Churn/dormancy
Ideally, every customer’s lifecycle would settle into the advocacy phase in perpetuity, but sometimes regular customers stop purchasing a product or abandon it for a competing product.
Marketers use several tactics to turn former customers into return customers, including: